Work with solutions¶
Here is an example* of work with the Cadbiom API to process the solutions obtained by a causality search.
*: see notes at the end of this page.
Solutions handling¶
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
# Fix print function for Dino-Python
from __future__ import print_function
#import mpld3
#mpld3.enable_notebook()
Let’s define a function to get entities (boundaries) in Minimal Activation Conditions (MAC) from *mac.txt files. The command line package offers high level functions to process such data.
[2]:
from cadbiom_cmd.tools.solutions import get_all_macs
def load_macs(filepath):
"""Return a set of entities in all MAC lines from a directory or from a file"""
# Get MAC lines from a file
return set(frozenset(mac.split()) for mac in get_all_macs(filepath))
Venn diagram¶
Thanks to the package matplotlib_venn we can quickly design relationships between sets of boundaries accross multiple queries:
[3]:
from matplotlib_venn import venn3
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import itertools as it
def venn(files):
"""Display a Venn diagram to show relationships between sets of boundaries
in the given files.
:param files: Dictionary of filepaths as keys and corresponding titles as values
(titles will be printed for the corresponding areas in the diagram).
Ex: ``{filepath1: "Query 1"}``
:type files: <dict>
"""
places = {title: set(it.chain(*load_macs(filepath))) for filepath, title in files.items()}
# Tweak the size of the plot
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
venn3(places.values(), places.keys())
venn({
"_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2 and PERP_mac.txt": "MMP2 and PERP",
"_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2_mac.txt": "MMP2",
"_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_PERP_mac.txt": "PERP",
})
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2 and PERP_mac.txt> Number of MACS loaded: 400
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2 and PERP_mac.txt> Number of unique MACS returned: 400
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_PERP_mac.txt> Number of MACS loaded: 10
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_PERP_mac.txt> Number of unique MACS returned: 10
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2_mac.txt> Number of MACS loaded: 400
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2_mac.txt> Number of unique MACS returned: 400
/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/matplotlib_venn/_venn3.py:117: UserWarning: Bad circle positioning
warnings.warn("Bad circle positioning")
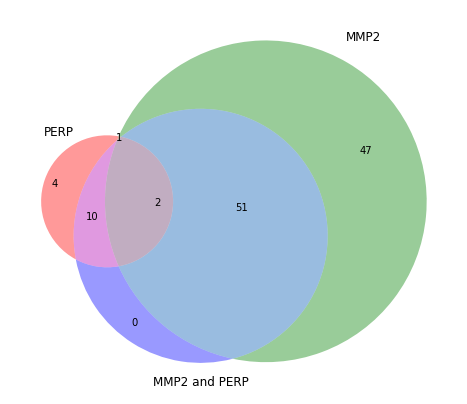
Get content of areas¶
In order to know the places in each subset, we define a new function capable of additionally taking an infinite number of input files (Venn diagram are limited on this point).
[4]:
from copy import deepcopy
def venn_data(files):
"""Display the content of areas of the venn diagram built from sets of
boundaries in the given files.
Example with 3 files (7 independent sets):
- PERP & MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP
- PERP & MMP2 - (PERP & MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP)
- PERP & MMP2 and PERP - (PERP & MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP)
- MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP - (PERP & MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP)
- PERP
- MMP2
- MMP2 and PERP
:param files: Dictionary of filepaths as keys and corresponding titles as values
(titles will be printed for the corresponding areas in the diagram).
Ex: ``{filepath1: "Query 1"}``
:type files: <dict>
:return: Dictionary of boundaries per subsets.
Names of subsets as keys; subsets as values.
:rtype: <dict <str>:<set>>
"""
result = dict()
boundaries = {title: set(it.chain(*load_macs(filepath))) for filepath, title in files.items()}
common_boundaries = set.intersection(*boundaries.values())
result[" & ".join(boundaries.keys())] = common_boundaries
uniq_places = deepcopy(boundaries)
for (file_1, places_1), (file_2, places_2) in it.combinations(boundaries.items(), 2):
pair_common_boundaries = places_1 & places_2
intersect = pair_common_boundaries - common_boundaries
# Intersections
result[file_1 + " & " + file_2] = intersect
# Prune specific places of the 2 distinct files
uniq_places[file_1] -= pair_common_boundaries
uniq_places[file_2] -= pair_common_boundaries
# Handle specific places (places that only belong to 1 file)
for file, macs in uniq_places.items():
result[file] = macs
return result
subsets = venn_data({
"_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2 and PERP_mac.txt": "MMP2 and PERP",
"_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2_mac.txt": "MMP2",
"_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_PERP_mac.txt": "PERP",
})
# Display subsets content
# Use compact=True on Python3 for nicer output
import pprint
pprint.pprint(subsets)
# Count boundaries in each subset
{k: len(v) for k, v in subsets.items()}
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2 and PERP_mac.txt> Number of MACS loaded: 400
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2 and PERP_mac.txt> Number of unique MACS returned: 400
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_PERP_mac.txt> Number of MACS loaded: 10
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_PERP_mac.txt> Number of unique MACS returned: 10
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2_mac.txt> Number of MACS loaded: 400
INFO: <_static/demo_files/EMT2_results/model_pid_mars_fix_p53_without_scc_MMP2_mac.txt> Number of unique MACS returned: 400
{'MMP2': set(['ASK1',
'CD147',
'CD40L__trimer__integral_to_membrane',
'CD40_integral_to_membrane',
'CDC42_GDP_1ina',
'CXCL10_extracellular_region',
'CXCL11_extracellular_region',
'CXCL4',
'CXCL9_extracellular_region',
'CXCR3_B_integral_to_membrane',
'CaM_Ca2__CAMKIIB_1act',
'Cyclophilin_B',
'DAG_v1',
'ErbB4_ErbB4_neuregulin_1_beta_neuregulin_1_beta_GRB2_SHC_1act_integral_to_membrane_v1',
'Erk2_cytoplasm',
'GCAP_Family_Ca____1ina_cytoplasm',
'GCKR_1act',
'GCK_1act',
'GLK_1act',
'IL2_extracellular_region_gene',
'LPS',
'MEK1',
'MEK1_MEK2_v4',
'MEK2',
'MEKK1',
'NESK_1act',
'NRAGE',
'OSM_MEKK3_cytoplasm',
'Osteopontin_extracellular_region',
'PGD2_DP',
'PGI2_IP',
'PKC',
'PKC_beta',
'PKC_isoenzymes',
'PRKACA',
'PSD95',
'RAF1_1O_5O_1act_plasma_membrane',
'RAF1_4O_1act_plasma_membrane',
'Rac1_plasma_membrane',
'Syk',
'Syndecan_1',
'TNIK_1act',
'TRAF2',
'TRAF2_cytoplasm',
'TRX_ASK1_1ina',
'VEGFR3_VEGFC_D_1act',
'proNGF__dimer__extracellular_region']),
'MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP': set(['AES_LEF1_1act_nucleus',
'ASK1_ASK2_1act',
'ATF2',
'ATF2_1ina',
'ATF2_1ina_cytoplasm',
'COT',
'DLK',
'E2_integral_to_membrane',
'ER_alpha_Gai_GDP_Gbeta_gamma_1act_plasma_membrane',
'E_cadherin_Ca2__beta_catenin_gamma_catenin_alpha_catenin_p120_catenin_cell_cell_junction_v1',
'Erk2',
'FGF2_extracellular_region',
'FGFR_FGF2_complex',
'FOXM1B_nucleus',
'Fra1_1O_2O_nucleus',
'Gamma_Secretase_1act',
'HDAC1_LEF1_1act_nucleus',
'JAM_A',
'JNK',
'JNK2',
'JUNB_nucleus',
'JUN_2O_2O_nucleus',
'LPA',
'LPA1_plasma_membrane',
'MAPK_14',
'MAPK_14_cytoplasm',
'MEK1_cytoplasm',
'MEKK3',
'MEP1B_1act_integral_to_membrane',
'MKK3',
'MKK4',
'MKK4_cytoplasm',
'MKK6',
'MKK7',
'MLK2_1act',
'MMP2_gene',
'PAK1',
'PAK2',
'PRL_3',
'RAC1_CDC42_GTP_1act_plasma_membrane',
'RIP_cytoplasm',
'TGFB1__dimer__1act_extracellular_region',
'TLE1_LEF1_1act_nucleus',
'TLE2_LEF1_1act_nucleus',
'TRAIL__trimer__extracellular_region',
'alphav_beta3_Integrin',
'beta_APP',
'ceramide',
'cortisol',
'p38_beta_cytoplasm',
'p38_gamma']),
'MMP2 and PERP': set([]),
'PERP': set(['MDM2_KAP1_nucleus',
'NRIF',
'p53_1a_nucleus',
'proBDNF__dimer__extracellular_region']),
'PERP & MMP2': set(['Sortilin']),
'PERP & MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP': set(['TRAF6',
'p75_NTR__1N_integral_to_membrane']),
'PERP & MMP2 and PERP': set(['Cables',
'NQO1',
'PERP_gene',
'PML_YAP1',
'PML_gene',
'TAp63a__tetramer__nucleus',
'TAp63g__tetramer__nucleus',
'TAp73a__tetramer__nucleus_v3',
'dNp63a__tetramer__nucleus_v2',
'p300'])}
[4]:
{'MMP2': 47,
'MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP': 51,
'MMP2 and PERP': 0,
'PERP': 4,
'PERP & MMP2': 1,
'PERP & MMP2 & MMP2 and PERP': 2,
'PERP & MMP2 and PERP': 10}
Notes¶
About the use of Jupyter showed in this page:
Jupyter is a fancy tool but it allows to execute Python code block by block, in a global context (i.e., with variables that persist and will be mutated in that context, execution after execution). This is a very bad working practice that is however encouraged by this kind of tool and by IDEs unfortunately offered to beginners (Spyder for example).
These methods are directly inherited from the practices of the community using the R language and the RStudio “IDE”. To avoid side effects such as persistence of variables, one MUST reset the console/notebook between runs by reloading the kernel as often as possible. Whilst this may seem redundant or heavy, it’s an extremely effective method of reducing unwanted side effects and bugs in your code.